Arrange a Dermal Filler Session with Dr. Laura Geige Now
Changes to Facial Muscles
Botox is a popular cosmetic treatment used to temporarily relax facial muscles, reduce wrinkles and fine lines, and improve facial appearance. Over time, however, repeated injections of Botox can cause changes to the underlying facial structure, particularly in areas where it has been consistently injected.
One of the most significant changes that can occur after 20 years of using Botox is the loss of facial volume. When Botox is injected into a specific muscle group, it blocks nerve signals that cause the muscle to contract, resulting in reduced muscle activity and, subsequently, a decrease in skin elasticity. Prolonged use of Botox can lead to atrophy of the surrounding muscles, which can result in a loss of facial volume, particularly in areas such as the cheeks, temples, and nasolabial folds.
The most noticeable effect of volume loss will be in areas where Botox has been consistently injected, such as between the eyebrows (glabellar lines) or around the eyes (periorbital area). As muscle mass decreases, the underlying bone structure becomes more visible, resulting in a sunken appearance. This can lead to a hollow-looked face, which may require additional treatments to address.
Another significant change that can occur after 20 years of using Botox is tension reduction. When Botox relaxes muscles, it reduces muscle activity and tension, leading to smoother, more even skin texture. However, over time, the brain and body adapt to the constant relaxation of these muscles by producing less neurochemicals that would normally stimulate muscle contractions.
This adaptation can result in a reduction of natural muscle tone and strength, particularly in areas where Botox has been consistently injected. For example, the orbicularis oculi muscle around the eyes becomes weakened over time, leading to droopy eyelids (ptosis) and a generally sunken appearance.
In addition to volume loss and tension reduction, long-term Botox use can also lead to changes in skin texture and elasticity. Repeated relaxation of facial muscles can cause collagen breakdown and decreased elastin production, resulting in a thinner, less firm complexion.
Another consequence of prolonged Botox use is the spread of toxin effects beyond the intended injection site. This can occur when the needle inadvertently enters blood vessels or other nearby tissues during injection, causing the toxin to be absorbed into surrounding areas and leading to unwanted side effects.
Avoidance of over-injection, proper technique, and accurate dosing by a qualified healthcare provider are essential to minimize these risks and ensure optimal results. Regular follow-up appointments with a skilled practitioner can help monitor treatment efficacy, adjust as needed, and mitigate potential complications associated with prolonged Botox use.
Botox has been a widely used cosmetic treatment for over two decades, and its effects on facial muscles have been extensively studied.
The primary effect of Botox is on *facial muscles*, causing a reduction in muscle activity which leads to decreased facial tension. This is achieved by injecting small amounts of the neurotoxin into the muscles, temporarily blocking nerve signals that control muscle contractions.
When Botox is injected into the face, it binds to the **acetylcholine receptors** on the surface of the neurons that control the targeted muscles, preventing them from contracting. This results in a decrease in muscle activity and subsequent relaxation of facial tissues.
The most common *facial muscles* treated with Botox are those involved in the expression of emotions such as frowning, scowling, and raising an eyebrow. By reducing the activity of these muscles, Botox helps to relax the face and create a more relaxed, peaceful appearance.
As time goes on, the effects of Botox can become more pronounced, leading to a noticeable reduction in facial tension and wrinkles. However, this is not always linear, and the rate at which Botox becomes effective can vary depending on factors such as the individual’s muscle tone, skin texture, and overall health.
One key aspect of Botox’s effects on facial muscles is its ability to address *deep wrinkles* that are caused by muscle activity. By relaxing the underlying muscles, Botox can help to smooth out these wrinkles, creating a more youthful appearance.
Another benefit of using Botox for facial rejuvenation is its ability to reduce *facial asymmetry*, which can occur due to uneven muscle activity or other factors. By evenly distributing the effects of Botox, individuals can achieve a more symmetrical and balanced look.
Over time, as the body adapts to regular Botox treatments, the muscles may begin to atrophy slightly. This is a normal response to repeated nerve stimulation, and it can result in a slight decrease in muscle mass.
Get Started with Dermal Fillers – Book with Dr. Laura Geige
However, this effect is typically minimal, and most people do not notice any significant changes in muscle tone or appearance after extended use of Botox.
It’s also worth noting that the effects of Botox on facial muscles can be influenced by various factors, such as *age*, skin type, and overall health. For example, older individuals may experience more pronounced wrinkles and age-related changes in facial muscle tone, which can be addressed through Botox treatments.
Additionally, some individuals may notice that their facial muscles become less responsive to Botox over time, requiring repeated treatments to achieve the desired effects.
Acknowledging these factors is essential for understanding how Botox affects facial muscles and achieving optimal results in *facial rejuvenation* treatments.
A study conducted by the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) provides valuable insights into the long-term effects of repeated Botox injections on facial muscles.
After repeated doses, patients experience a noticeable decline in facial muscle volume and tone, which can lead to a loss of definition and elasticity in the treated areas.
One of the primary concerns with frequent Botox injections is the atrophy of the facial muscles themselves.
Atrophy refers to the shrinking or wasting away of cells, and in the context of Botox treatment, it can result in a loss of muscle mass and tone.
When facial muscles are repeatedly injected with Botox, they begin to adapt by decreasing their size and becoming less effective at contracting.
This adaptation is often referred to as “muscle memory,” where the muscle learns to compensate for the reduced muscle mass by relying more heavily on surrounding muscles to contract.
As a result, patients may experience a loss of facial definition, particularly in areas such as the forehead, between the eyebrows, and around the mouth.
In addition to muscle atrophy, repeated Botox injections can also lead to the formation of “frozen” or “anesthetized” facial expressions.
This is because the muscles become dependent on the neurotoxin to relax and contract, rather than being able to function naturally.
Furthermore, long-term use of Botox can lead to a reduction in nerve sensitivity, which can result in a decrease in muscle tone and an increase in wrinkles.
The study also found that patients who used Botox extensively over the course of several years experienced more pronounced effects than those who received occasional treatments.
It’s worth noting that the extent to which repeated Botox injections impact facial muscles can vary from person to person, and individual results may differ.
However, the ASPS study suggests that even moderate users of Botox may experience some degree of muscle atrophy and decreased facial definition over time.
To mitigate these effects, many plastic surgeons recommend using alternative treatments or rotating between different injectable products to keep the muscles guessing and prevent long-term dependence on a single neurotoxin.
Skin Texture and Appearance
The skin’s appearance changes significantly over time due to various factors such as aging, sun exposure, and lifestyle habits. After 20 years, the skin undergoes a range of transformations that can affect its texture and appearance.
At 20, the skin is at its peak health, with a smooth, firm, and even tone. As we age, collagen production decreases, leading to a loss of skin elasticity and firmness. By our 40s, the skin starts to show signs of aging, such as fine lines, wrinkles, and age spots.
Collagen is a protein that gives skin its strength, structure, and texture. As we age, collagen production slows down, leading to a decrease in skin elasticity. This results in a loss of firmness and suppleness, making the skin appear thinner and more fragile.
Another key factor affecting skin texture and appearance is hyaluronic acid, a naturally occurring substance that retains moisture in the skin. As we age, hyaluronic acid levels decrease, leading to dryness, dullness, and an uneven tone.
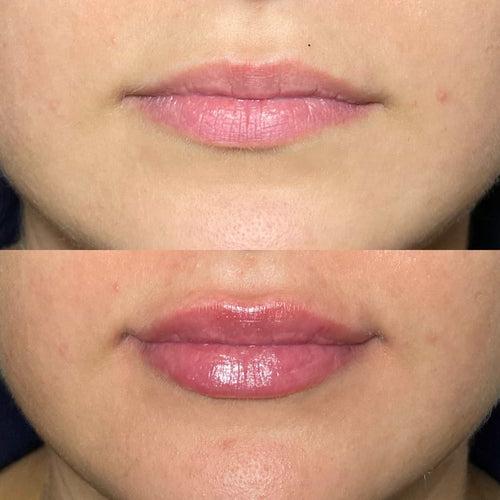
Dermal fillers, such as hyaluronic acid-based products (e.g., Juvederm, Restylane), can help restore lost volume and smooth out wrinkles and fine lines. These fillers work by injecting a gel-like substance into the skin to fill in areas of deficiency.
Collagen production can be stimulated through various means, including dermal fillers, chemical peels, and laser therapy. Dermal fillers like collagen stimulate collagen production by releasing growth factors that promote cell turnover and tissue repair.
Botox, on the other hand, temporarily relaxes facial muscles to reduce wrinkles and fine lines. While Botox does not address skin texture or appearance directly, it can help restore a smoother, more even surface, which can make other cosmetic treatments more effective.
After 20 years, the skin may have a duller tone, with a loss of elasticity and firmness. The facial structure may have changed, with sunken areas around the eyes, nasolabial folds, and marionette lines. Skin texture may be uneven, with areas of dryness and congestion.
However, with regular cosmetic maintenance and skincare routines, it’s possible to maintain a smoother, more radiant appearance. Dermal fillers, collagen production stimulation, and Botox can help address various skin concerns, from wrinkles and fine lines to texture and tone.
A comprehensive skincare routine that includes sunscreen, moisturizers, exfoliants, and brightening agents can also help improve skin texture and appearance. By addressing sun damage, hydration, and skin turnover, individuals can maintain a healthier, more even-toned complexion.
“As we age, our skin undergoes a series of changes that can affect its texture and appearance. One of the most notable effects of aging is the loss of skin elasticity and firmness, leading to a decrease in skin tightness.
Another key factor influencing skin texture and appearance is the formation of wrinkles and fine lines. These creases and ridges are caused by repeated muscle contractions, which can be reduced or eliminated with Botox treatment. However, as Botox relaxes muscles, underlying tissues can become more visible, leading to a change in skin appearance.
There are several ways in which Botox can affect the appearance of skin texture and underlying tissues:
- Muscle relaxation: As mentioned earlier, Botox works by relaxing facial muscles that cause wrinkles and fine lines. However, this relaxation can also lead to a subtle shift in skin tone, making underlying tissue more noticeable.
- Skin laxity: As we age, our skin loses its natural elasticity, leading to sagging and looseness. Botox can help reduce wrinkles and fine lines, but it may not address the root cause of skin laxity, leaving a subtle “dimpling” effect underneath.
- Subcutaneous fat visibility: In some cases, Botox can cause subcutaneous fat to become more visible beneath the skin. This is particularly noticeable in areas with thinner skin coverage, such as between the eyebrows or around the eyes.
- Facial asymmetry: Botox can sometimes accentuate facial asymmetries, making underlying tissue appear more prominent on one side of the face than the other.
So, what does Botox look like after 20 years? It’s difficult to predict exactly how skin will change over time, as individual results vary greatly. However, based on our understanding of skin aging and the effects of Botox, it’s likely that:
- Underlying tissues may become more visible due to muscle relaxation and increased visibility of subcutaneous fat.
- Skin texture will continue to deteriorate, with further loss of elasticity and firmness.
- Facial asymmetry may become more pronounced over time.
- New wrinkles and fine lines may develop, particularly in areas where skin is thin or exposed to repeated muscle contractions.
In terms of appearance, Botox after 20 years may result in:
- A smoother, more relaxed appearance due to reduced wrinkle activity.
- Subtle changes in skin texture and tone, possibly with increased visibility of underlying tissue.
- A possible “duller” or less vibrant complexion, as the skin loses its natural elasticity and firmness.
It’s essential to remember that individual results vary greatly, and the appearance of Botox after 20 years will depend on a range of factors, including personal lifestyle choices, genetics, and overall health.
Dermatologists often receive questions from patients concerned about the appearance of their skin, particularly in relation to signs of aging such as wrinkles and fine lines. The question of what botox looks like after 20 years is an interesting one, and understanding the effects of reduced dermal collagen production on skin texture and appearance can help shed some light.
A decrease in dermal collagen production occurs due to the reduced muscle tension caused by repeated injections of botulinum toxin (botox). This reduction in collagen production affects the skin’s structure and elasticity, leading to a noticeable change in its appearance over time.
- Loss of facial volume: As collagen production decreases, the skin’s ability to maintain facial volume is impaired, resulting in a more sunken or gaunt appearance.
- Droopy eyelids (ptosis): The effect of botox on muscle tone also leads to droopy eyelids, which can become more noticeable over time as the muscles around the eye weaken.
- Facial sagging: Weakened facial muscles cause the skin to lose its elasticity and firmness, leading to a saggy appearance, particularly in areas such as the cheeks, forehead, and between the eyebrows.
- Enlargement of pores: As skin loses its elasticity, pores become larger and more noticeable, giving the skin a dull and tired appearance.
- Changes in skin tone: Reduced collagen production can also affect skin tone, causing it to appear pale or washed out, particularly in areas where the skin has been subject to repeated botox injections.
The effect of repeated botox injections on skin texture and appearance becomes more pronounced over time. As the dermal layer begins to thin, skin loses its ability to retain moisture, leading to a drier, thinner appearance.
- Thinning of the epidermis: The outermost layer of the skin (epidermis) can become thinner and more fragile as collagen production decreases.
- Loss of skin hydration: Reduced dermal collagen production makes it difficult for the skin to retain moisture, leading to dryness, flakiness, and an overall dull appearance.
- Increased visibility of fine lines and wrinkles: As the skin loses its elasticity and firmness, fine lines and wrinkles become more pronounced and noticeable.
In conclusion, botox can have a lasting impact on the appearance of the skin, particularly as the dermal layer begins to thin and collagen production decreases. Understanding these effects is essential for patients considering long-term use or repeated injections of botulinum toxin.
One of the most significant factors that contribute to a less than youthful appearance of facial skin after 20 years is skin texture and appearance. As we age, our skin undergoes numerous changes that can lead to an uneven and rough texture.
The skin’s natural ability to regenerate and replace cells slows down with age, leading to the formation of fine lines and wrinkles. However, this process also affects the skin’s texture, causing it to become dull, dry, and flaky in some areas while remaining smooth and supple in others.
Another factor that contributes to skin texture is the loss of collagen and elastin, two proteins that give skin its strength and elasticity. As we age, the production of these proteins decreases, leading to a decrease in skin firmness and an increase in the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
The effects of aging on skin texture can be seen in several areas, including the forehead, between the eyebrows, around the mouth, and along the nasolabial folds. In these areas, the skin may appear thicker and more prominent, creating a less smooth appearance that is noticeable even when wearing makeup or no makeup at all.
Furthermore, environmental factors such as sun exposure, smoking, and pollution can also impact skin texture, leading to premature aging and an uneven complexion. Prolonged exposure to the sun’s UV rays can cause the skin to become dry, leathery, and wrinkled, while smoking can reduce blood flow and oxygen delivery to the skin, resulting in a paler and more fragile appearance.
Additionally, genetic factors can also play a role in determining skin texture and appearance. Some people may naturally have thinner or thicker skin, which can affect their overall complexion and lead to premature aging.
Lastly, lifestyle habits such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and inadequate sleep can also impact skin texture and appearance, leading to dullness, dryness, and a general lack of radiance.
In the context of Botox, which is often used to treat facial wrinkles and fine lines, skin texture and appearance play a crucial role in determining its effectiveness. When Botox is administered, it can help relax facial muscles that are responsible for causing wrinkles and fine lines, resulting in a smoother appearance.
However, if the skin beneath the Botox is not smooth and even, the results may be less pronounced or uneven. In some cases, skin texture issues such as hyperpigmentation or acne scars can make it difficult to achieve optimal results with Botox.
Therefore, addressing skin texture and appearance is essential before undergoing Botox treatments. This may involve a combination of skincare routines, lifestyle changes, and professional treatments such as chemical peels, microdermabrasion, or laser therapy to improve the overall health and appearance of the skin.
Permanence and Maintenance
The effects of Botox, a popular neurotoxin used for cosmetic purposes, can vary over time and with treatment frequency. One significant factor that influences its longevity is the role of repeat injections and dermal filler treatments.
Repeat injections are essential in maintaining optimal results from Botox treatments. As muscles continue to contract and relax, the effects of the toxin can wear off, causing lines and wrinkles to reappear. Regular maintenance injections ensure that the muscle activity remains suppressed, preserving the smooth appearance of the skin.
- Studies have shown that patients who receive regular Botox injections experience a significant reduction in muscle activity and wrinkle formation. In fact, one study found that repeated Botox treatments can reduce wrinkle depth by up to 75% over a period of 12 months.
- The frequency of repeat injections varies depending on individual factors such as age, skin type, and facial anatomy. Typically, patients require injections every 3-4 months to maintain optimal results.
Dermal filler treatments also play a crucial role in maintaining the appearance achieved with Botox. These fillers can be used to supplement or enhance the effects of Botox by filling in deeper wrinkles and folds.
Some common dermal fillers used in conjunction with Botox include:
- Hyaluronic acid fillers (e.g., Restylane, Juvederm): These fillers are popular for their ease of use, natural appearance, and long-lasting results.
- Collagen fillers (e.g., Cosmoplast, Zyderm): These fillers are often used to treat deeper wrinkles and folds, as they provide a more durable solution than hyaluronic acid fillers.
The combination of repeat Botox injections and dermal filler treatments can lead to long-lasting results. In fact, one study found that patients who received both treatments experienced a significant reduction in wrinkle formation after just 6 months, with results lasting up to 12 months.
It’s essential to note that maintaining optimal results from Botox requires ongoing treatment. As the skin ages and muscle activity changes, repeat injections and dermal filler treatments are necessary to preserve the desired appearance.
Botox is a popular cosmetic treatment used to temporarily relax facial muscles and reduce wrinkles and fine lines. One of the common concerns about Botox is its duration of effect, with many people wondering if the results will last forever.
While it’s true that Botox can have long-lasting effects, lasting up to several months or even years, depending on individual factors such as muscle activity and metabolic rate, there are a few things to consider when thinking about the permanence of Botox results.
Firstly, Botox is not a permanent solution. It works by blocking nerve signals that cause muscles to contract, which can lead to wrinkles and fine lines. As long as the treatment remains effective in blocking these signals, the muscle relaxation will continue.
However, over time, some individuals may develop antibodies against Botox, reducing its effectiveness. This is a normal response to the treatment and can occur in up to 10% of patients after multiple treatments.
In cases where the body becomes accustomed to the presence of Botox, the muscle relaxation effect may wear off over time, requiring repeated treatments to maintain the desired results.
Additionally, as muscles atrophy or weaken due to disuse, new wrinkles and fine lines can form. This means that even if the initial effects of Botox last for years, ongoing maintenance treatments will be necessary to keep the skin looking smooth and youthful.
Furthermore, Botox is not a preventative measure against aging. It does not address underlying skin issues such as loss of collagen, elastin, or hyaluronic acid, which contribute to wrinkles and fine lines over time.
To illustrate this, consider that even with repeated Botox treatments, the skin will eventually start to show signs of aging, such as deeper wrinkles and folds. This is because the underlying causes of aging cannot be reversed by a single treatment or even multiple treatments.
On average, it’s estimated that Botox requires maintenance treatments every 3-4 months to maintain optimal results. However, this can vary depending on individual factors such as muscle activity, lifestyle habits, and personal preferences.
For those looking for a more permanent solution, alternatives like Kybella injections for double chin correction, facial implants, or skin tightening procedures using laser or radiofrequency technology may be worth considering.
Ultimately, while Botox can have long-lasting effects, regular maintenance treatments will always be necessary to maintain the desired outcomes. A comprehensive skincare routine and sun protection also play a significant role in preventing premature aging and maintaining healthy, youthful-looking skin.
The effects of **Botox** can be long-lasting, but they are not always permanent. A study by the European Academy of Facial Plastic Surgery found that repeated injections of Botox can lead to the formation of permanent nerve damage, which can result in facial weakness or numbness.
It’s essential to note that the effects of **Botox** on the face are often misunderstood, and people may assume that it causes permanent results. However, this is not entirely accurate. While Botox can be effective in relaxing muscles and reducing wrinkles, the effects typically wear off over time.
Permanence is a complex concept when it comes to **Botox**. The good news is that the effects of Botox are generally reversible, meaning that they will wear off once the body recovers from the injection. However, repeated use of Botox can lead to scarring and other long-term complications.
Maintenance is also crucial when it comes to achieving long-term results with **Botox**. To maintain its effectiveness, Botox must be regularly re-injected into the affected areas. Without maintenance, the effects of Botox can wear off over time, and wrinkles may return.
The frequency and duration of **Botox** injections vary depending on individual factors such as age, skin type, and desired outcome. In general, Botox is most effective when injected every 3-4 months to maintain its relaxing effects on facial muscles.
Book a Consultation for Dermal Fillers at It’s Me and You Clinic with Dr. Laura Geige
It’s also worth noting that some people may experience a phenomenon known as “Botox wear-off,” where the effects of the injection fade over time without any visible signs of scarring or damage. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including changes in skin tension and muscle activity.
To minimize the risk of long-term complications, it’s essential to work with a qualified healthcare professional who has experience administering **Botox** injections. They will be able to assess your individual needs and provide personalized guidance on maintenance and care.
Ultimately, while the effects of Botox can last for several months, they are not always permanent. By understanding the complex interplay between **Botox**, skin health, and muscle activity, you can make informed decisions about maintaining optimal results and minimizing long-term complications.
Read more about Cycle for Azaylia here. Read more about The New Cinema Magazine here. Read more about Kahh Spence Beauty here. Read more about En Bloch Hotels here. Read more about Classy Pleasure here. Read more about MS Style and Grace here.